Reprints of the Titanic and History Print
Inv# SS1113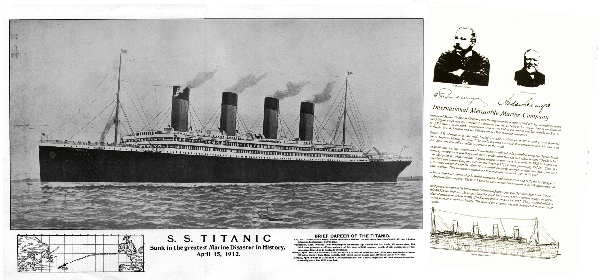
RMS Titanic was a British passenger liner that sank in the North Atlantic Ocean in the early hours of 15 April 1912, after colliding with an iceberg during her maiden voyage from Southampton to New York City. There were an estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, and more than 1,500 died, making it one of the deadliest commercial peacetime maritime disasters in modern history. RMS Titanic was the largest ship afloat at the time she entered service and was the second of three Olympic-class ocean liners operated by the White Star Line. She was built by the Harland and Wolff shipyard in Belfast. Thomas Andrews, chief naval architect of the shipyard at the time, died in the disaster. Titanic was under the command of Capt. Edward Smith, who also went down with the ship. The ocean liner carried some of the wealthiest people in the world, as well as hundreds of emigrants from Great Britain and Ireland, Scandinavia and elsewhere throughout Europe who were seeking a new life in the United States. The first-class accommodation was designed to be the pinnacle of comfort and luxury, with an on-board gymnasium, swimming pool, libraries, high-class restaurants and opulent cabins. A high-powered radiotelegraph transmitter was available for sending passenger "marconigrams" and for the ship's operational use. Although Titanic had advanced safety features such as watertight compartments and remotely activated watertight doors, it only carried enough lifeboats for 1,178 people—about half the number on board, and one third of her total capacity—due to outdated maritime safety regulations. The ship carried 16 lifeboat davits which could lower three lifeboats each, for a total of 48 boats. However, Titanic carried only a total of 20 lifeboats, four of which were collapsible and proved hard to launch during the sinking. After leaving Southampton on 10 April 1912, Titanic called at Cherbourg in France and Queenstown (now Cobh) in Ireland before heading west to New York. On 14 April, four days into the crossing and about 375 miles (600 km) south of Newfoundland, she hit an iceberg at 11:40 p.m. ship's time. The collision caused the hull plates to buckle inwards along her starboard (right) side and opened five of her sixteen watertight compartments to the sea; she could only survive four flooding. Meanwhile, passengers and some crew members were evacuated in lifeboats, many of which were launched only partially loaded. A disproportionate number of men were left aboard because of a "women and children first" protocol for loading lifeboats. At 2:20 a.m., she broke apart and foundered with well over one thousand people still aboard. Just under two hours after Titanic sank, the Cunard liner RMS Carpathia arrived and brought aboard an estimated 705 survivors. The disaster was met with worldwide shock and outrage at the huge loss of life and the regulatory and operational failures that led to it. Public inquiries in Britain and the United States led to major improvements in maritime safety. One of their most important legacies was the establishment in 1914 of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), which still governs maritime safety. Additionally, several new wireless regulations were passed around the world in an effort to learn from the many missteps in wireless communications—which could have saved many more passengers. The wreck of Titanic was discovered in 1985 (more than 70 years after the disaster), during a US military mission[10] and remains on the seabed. The ship was split in two and is gradually disintegrating at a depth of 12,415 feet (3,784 m). Thousands of artefacts have been recovered and displayed at museums around the world. Titanic has become one of the most famous ships in history; her memory is kept alive by numerous works of popular culture, including books, folk songs, films, exhibits, and memorials. Titanic is the second largest ocean liner wreck in the world, only beaten by her sister HMHS Britannic, the largest ever sunk, although she holds the record as the largest sunk while actually in service as a liner due to Britannic being used as a hospital ship at the time of her sinking. The final survivor of the sinking, Millvina Dean, aged two months at the time, died in 2009 at the age of 97. (Wikipedia) We’ve found a rare 1912 print of the Titanic. This reprint is on thick cream colored card stock (15”x 27.5”). It includes details of the disaster including map, number of passengers, etc. Plus another large print with a side view of the Titanic and its history. Large and so Historic!
The International Mercantile Marine Company, originally the International Navigation Company, was a trust formed in the early twentieth century as an attempt by J.P. Morgan to monopolize the shipping trade.
IMM was founded by shipping magnates Clement Griscom of the American Line and Red Star Line, Bernard N. Baker of the Atlantic Transport Line, J. Bruce Ismay of the White Star Line, and John Ellerman of the Leyland Line. The Dominion Line was also amalgamated. The project was bankrolled by J.P. Morgan & Co., led by financier J. P. Morgan. The company also had working profit-sharing relationships with the German Hamburg-Amerika and the North German Lloyd lines. The trust caused great concern in the British shipping industry and led directly to the British government's subsidy of the Cunard Line's new ships RMS Lusitania and RMS Mauretania in an effort to compete.
IMM was a holding company that controlled subsidiary corporations that had their own subsidiaries. Morgan hoped to dominate transatlantic shipping through interlocking directorates and contractual arrangements with the railroads, but that proved impossible because of the nature of sea transport, American antitrust legislation, and an agreement with the British government. One of IMM's subsidiaries was the White Star Line, which owned the RMS Titanic. Analysis of financial records shows that IMM was overleveraged and suffered from inadequate cash flow that caused it to default on bond interest payments in late 1914. As a result, a "friendly" receivership was put in effect in 1915, which allowed IMM to reorganize its finances; it emerged from the receivership in 1916. Saved by World War I, IMM eventually re-emerged, after a merger with Roosevelt Steamship Company, as the United States Lines, which itself went bankrupt in 1986.
A proposed subsidy bill in the United States Congress failed, as had become widely apparent by April 1902 and the company thus was never really successful. Beginning in the 1920s, the company underwent a series of corporate acquisitions and mergers, which resulted in its becoming the United States Lines in 1943.
As the shipping industry prospered in the late 19th century, some sought to create a trust that would monopolize U.S. shipping companies. However, all negotiations in this regard in the 1890s fell short. The intervention of John Pierpont Morgan, one of the richest men in the world, would change that.
The Atlantic Transport Line, owned by Bernard N. Baker and having both passenger and cargo ships, competed intensely with British and other shipping companies. Baker tried to sell his company to John Ellerman, chairman of the cargo-carrying Leyland Line, who had tried unsuccessfully to take possession of the Cunard Line and HAPAG, two powerful European companies. Negotiations between Baker and Ellerman, advanced but ultimately fell through.
Meanwhile, J. P. Morgan had already concluded agreements with Clement Griscom, president of the International Navigation Company, which operated the Red Star Line and the American Line. Finally, in December 1900, after six months of negotiations, the Atlantic Transport Line joined INC.
Subsequently, Baker, J. P. Morgan, and Simon Bettle Jr. (representative of the INC) negotiated with Ellerman, this time with a view to redeem his property. There would be two companies that would join the trust. The name of one of them was revealed in April 1901: the Leyland Line. The second turned out to be the prestigious White Star Line, bought by Morgan's team, after long negotiations, in April 1902. On 1 October 1902, JP Morgan & Co. announced the founding of the International Mercantile Marine Company, more commonly called IMM. (Constituent elements of IMM, including INC (chartered in 1871), had however been operating for many years already.) IMM was incorporated in New Jersey.
Morgan's role evolved over the years. Being American, he could not directly own British ships, but he could own the company that owned the ships. In 1902, the IMM carried 64,738 passengers, a total buoyed by high immigration to the United States. The IMM had signed a partnership with the two most important German shipping companies, Norddeutscher Lloyd and HAPAG, which carried a total of 66,838 passengers. The German-Morgan agreement, signed in New York on 20 February 1902, was a key step in the formation of what was to become the IMM, but did not fully address long-standing competitive friction between and amongst the major German and British transatlantic shipping companies.
Responses in the United Kingdom helped intensify these rivalries. Cunard Line, one of the British shipping companies with independent significance, received grants from the British government for the construction of two great ocean liners, the Lusitania and the Mauretania, which were placed into service in late 1907. The competitive response from the IMM group came in 1908 when Harland & Wolff was authorized to build the White Star Line's Olympic class ocean liner trio: RMS Olympic, RMS Titanic, and HMHS Britannic.
Since 1902, IMM had an agreement with James Pirrie, chairman of Harland & Wolff and member of the management of the White Star Line, stating that the vessels of the company will be built by Harland & Wolff for all the time. Ships of the company were also shifting from one company to another, like the Belgic, built for the White Star Line, which was transferred to the service of the Red Star Line under the name SS Belgenland (1914), or the Regina became the Westernland. This allowed the IMM to schedule a ship each day from the United Kingdom, and passengers to change their tickets to a position equivalent to another vessel of the company. Baker retired from the direction of the Atlantic Transport Line shortly after its integration with the IMM, and was replaced by Philip Franklin. He later became vice president of IMM, while Griscom was replaced as president by Joseph Bruce Ismay in 1904 (who was also president of the White Star Line).
The early 1910s marked a turning point for the IMM. Indeed, on 15 April 1912, the Titanic, flagship of its fleet, sank during her maiden voyage. Besides the financial and human losses, the sinking had repercussions on the organization of the trust. Through the American commission of inquiry devoted to the sinking, Senator William Alden Smith openly attacked the very principle of the company and Morgan. As had been arranged before Titanic sank, J. Bruce Ismay retired as president of IMM in 1913 and was succeeded by Harold Sanderson and Morgan died on 31 March 1913. After the 1915-16 receivership, Sanderson was succeeded as president by Franklin, who had been the receiver.
However, the sinking of the Titanic did not bring about the end of the IMM. Although theoretically powerful due to its continued influence with some of the top American, British, and German shipping companies, the overseeing company never managed to overcome its own financial problems, nor dominate the bulk of the North Atlantic shipping trade, and was therefore not as successful as expected. The company went into receivership in 1915 and was placed in the hands of Franklin, who managed to save it. In the late 1920s, he received grants from the government to American ships (built in the United States or flying the flag) and in 1926 it sold the White Star Line to the Royal Mail Steam Packet Company for £7 million, of which £2.35 million was still unpaid when the Royal Mail Group, which was overleveraged and undercapitalized, collapsed in the early 1930s. In 1930, IMM possessed 30 vessels. There were 19 in 1933 and only 11 by 1935.
The ailing company merged with the Roosevelt Steamship Company, parent company of the Roosevelt Line, in 1931 to form Roosevelt International Mercantile Marine Company (RIMM). Later in 1931, RIMM acquired the financially troubled United States Lines and began consolidating its operations under that brand. The Atlantic Transport Line was dissolved in late 1931 and its ships were distributed throughout RIMM's remaining divisions.
The American Line was merged into United States Lines in 1932, the Red Star Line was sold to Arnold Bernstein in 1934, Baltimore Mail Line merged into United States Lines in 1937, the Panama Pacific Line was dissolved in 1938 and its ships divested, and American Merchant Line was merged into United States Lines in 1938.
Finally, the Roosevelt Line was merged into United States Lines in 1940, leaving that company as RIMM's only remaining business. RIMM changed its name to United States Lines Inc. in 1943, recasting itself as a smaller company focused exclusively on transatlantic routes under a single brand.
Some businesses of the modern shipping industry still regard IMM as an early attempt at the corporate ownership of several companies under a single trust; the kind of large overseeing companies that dominate much of the maritime shipping world today.










Ebay ID: labarre_galleries